Introduction
The electricity demand in the South Asia region has consistently grown by more than five percent annually, with projections suggesting it will more than double by 2050. To meet this need on the path to net zero, the “Global Renewables and Energy Efficiency Pledge” calls on countries to “increase the global average annual rate of energy efficiency improvements from about 2% to more than 4% annually through 2030.” India is on the path to reduce emission intensity of its economy by 45% by 2030. As per IEA’s Sustainable Development Scenario, energy efficiency has the potential to abate 40% of the emissions by 2040.

Key Interventions
-
 Energy Efficiency for Indian Railways
Energy Efficiency for Indian Railways -
 Scaling Adoption of Energy Efficiency with EESL
Scaling Adoption of Energy Efficiency with EESL -
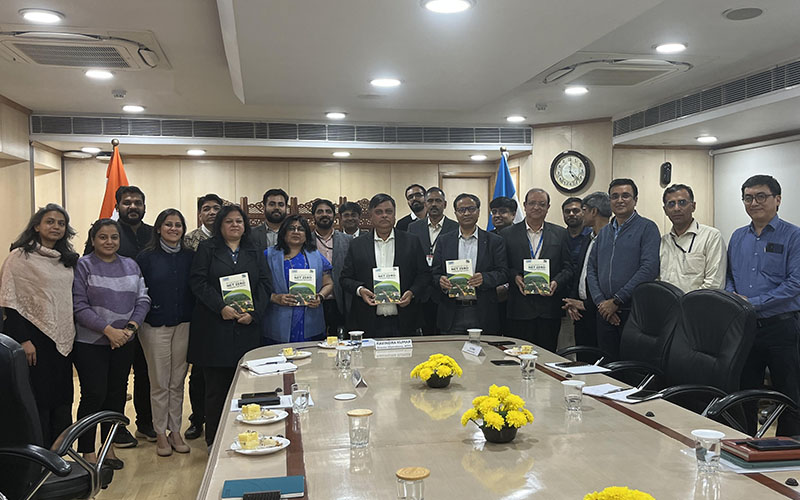
 Energy Efficiency for NTPCs’ Townships & Offices
Energy Efficiency for NTPCs’ Townships & Offices -
 Low Carbon Comfort Cooling
Low Carbon Comfort Cooling
-
 Energy Efficiency Initiatives in Bhutan and Maldives
Energy Efficiency Initiatives in Bhutan and Maldives -
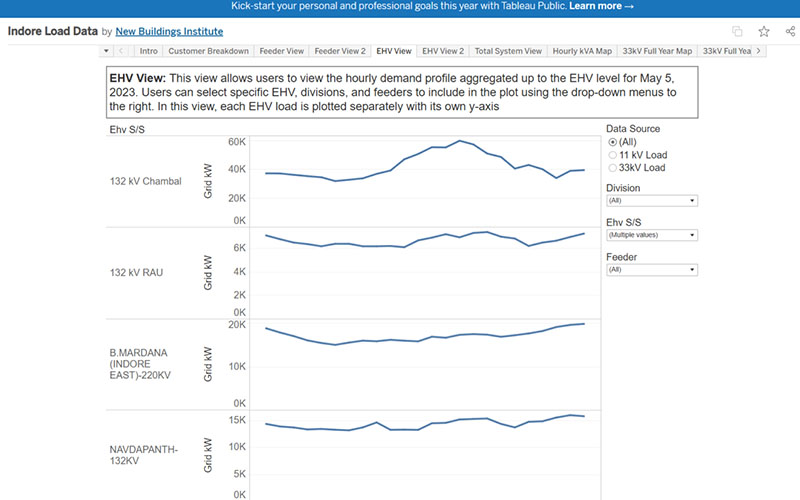
 Building-Grid Optimization
Building-Grid Optimization
- Developed Energy Efficiency Policy and Action Plan
- Managed the retrofit of over 2,500 buildings
- Ensured Super Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) compliance for all new buildings
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) Shunya / Shunya+ labelled buildings
- Procured energy efficient appliances
- Ensured integrated energy monitoring


- Developed Vision and Strategy 2030 for unlocking energy efficiency potential
- Ensured design and implementation of programs for buildings and cities
- Built various innovative business and financing models
- ‘Urjaveer’ initiative to build a network of energy efficiency champions across India, and make energy efficiency accessible and available at the grassroot level


- Developed Net Zero Roadmap for townships and offices
- Facilitated net zero township certification


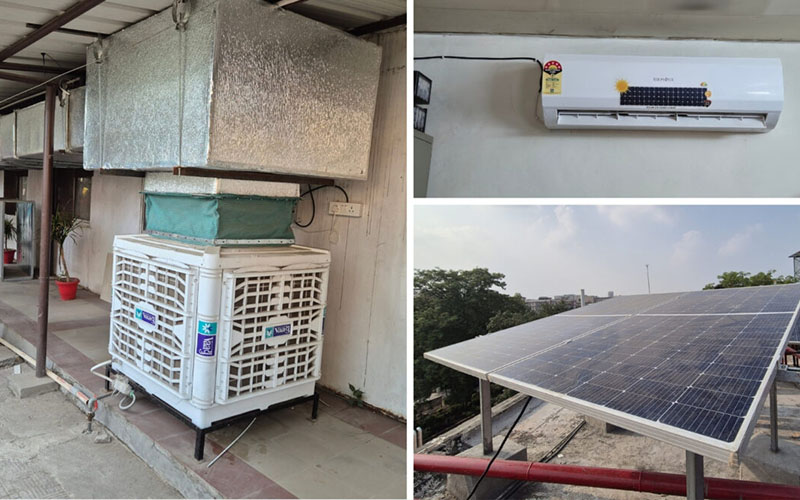
Heatwaves for countries in South Asia are 30 times more likely now, than 100 years ago. Over the next three decades the cooling demand is set to soar causing significant implications for electricity grids, GHG emissions, and urban heat islands. Energy efficient cooling will play an important role to achieve net zero emissions.
- Low Carbon Comfort and Cooling Collective (LC4)
- Scaling adoption of super-efficient cooling solutions with Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL) through Super-efficient air conditioner (SEAC) program and Chiller Energy Efficiency program
- Low carbon cooling pilots at Indian Railways’ Baroda House and Anand Vihar Railway Station, demonstrating scalable cooling technologies
- Global Ceiling Fan Competition with Indian Railways to revolutionize the ceiling fan market with innovative, highly durable, and energy-efficient solutions


- Development and roll-out of standards and labelling program of energy efficient appliances for Government of Bhutan
- Strengthening and expanding Maldives’ standard and labelling program
- Energy efficiency regulations for buildings and appliances in the Maldives
- Developed Maldives’ Energy Management Guide for Schools
- Hands on Energy Audit Program for certified energy audit in the Maldives


Buildings account for ~40% of energy related emissions. As per IEA, meeting the goals of the Paris Agreement will require buildings to improve energy intensity by 30-50% per sqm. Integrating energy efficiency and enabling demand flexibility for buildings is key for decarbonization.
- Grid Optimal Metrics for utilities in India
- South Asia’s first grid-interactive net zero energy building – TGREDCO (Telangana Renewable Energy Development Corporation Ltd.) office in Hyderabad
- Business models for better demand response and flexibility services
- Demand response initiatives with a leading utility for enhanced system resilience and efficiency

Key Achievements
Indian Railways’ Energy Efficiency Policy and Action Plan released and adopted across all railway zones with more than 6,200GWh life-time energy savings potential

Indian Railways’ Global Ceiling Fan Competition announced

NTPC’s Net Zero Roadmap (Townships and Offices) developed and adopted

Tender issued for energy audit of more than 1,150 energy-intensive buildings conducted for Indian Railways

Dialogue on green public procurement held with South Asia countries

Exposure visits conducted for officials from Bhutan to understand standards and labeling ecosystem in India

85,000 energy efficient ceiling fans and 9,000 5-star rated air conditioners procured by Indian Railways resulting in a lifetime energy savings of 83 GWh

EESL’s 2030 Strategy – “Enabling Net Zero” launched at CEM-14
Integrated SuperECBC requirement in tenders for 04 new railway station development

Tenders for procurement of 20,000 Super-Efficient Air conditioners released

Low Carbon Comfort Cooling Collective (LC4) launched at South Asia Clean Energy Forum (SACEF) 2024


