Introduction
The Government of India (GoI) has set for itself a target of
decreasing emissions intensity of its GDP by 45% in 2030 (from
2005 levels).
At present, the road transportation sector accounts for 12% of India s energy-related CO2 emissions. With the growing demand for private mobility and goods transportation, energy consumption and CO2 emissions from road transport is likely to double by 2050, as per IEA (International Energy Agency). The Government of India has recognized that reduction in road transport emissions would go a long way in attaining its emission reduction targets and has accordingly launched various schemes in the past.

Schemes Launched by the Government of India
Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric vehicles (FAME)
Production Linked Incentives
(PLI)
National Electric Bus Program (NEBP) and PM e-Bus Sewa for deployment of 50,000 electric buses
Although India has made significant strides in e-mobility, the following challenges remain:
Nascency of the sector and rapidly evolving technology
Uncertainty around useful life, salvage value and the lack of a secondary market
Limited availability of end-user financing options
Inadequate supporting infrastructure
SAREP, through its initiatives, is working with various public and private sector entities to support the realization of India's goals in the e-mobility sector.

Government of India has pledged that by 2030, 30% of all new vehicle sales in India will be electric and the cumulative investment requirement to achieve this target is around $200 bn.
South Asia - Targets to be Achieved
The South Asian countries, apart from India, have also pledged to transition towards e-mobility.
The major targets announced in e-mobility are as follows:
-
 India
India
-
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
-
 Bhutan
Bhutan
-
 Nepal
Nepal
-
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
-
 Maldives
Maldives
- GoI has pledged that by 2030, 30% of all new vehicle sales in India will be electric and the cumulative investment requirement to achieve this target is around $200 bns

- GHG emissions reduction by 4% in the transport sector through e-mobility and other measures
- Passenger cars: 20% by 2025 and 50% by 2030
- Buses: 10% by 2025, 50% by 2030
- Medium vehicles/trucks: 5% by 2025, 20% by 2030
- Heavy vehicles/trucks: 5% by 2030
- Private vehicle sales – 25% by 2025 and 90% by 2030
- 4W Passenger vehicle sales – 20% by 2025 and 60% by 2030
- Medium vehicles/trucks: 5% by 2025, 20% by 2030
- Develop 200 km of electric rail network

- Increase the share of EVs to at least 15% of all registered vehicles by 2030
- Net-zero emissions by 2030

Key Interventions
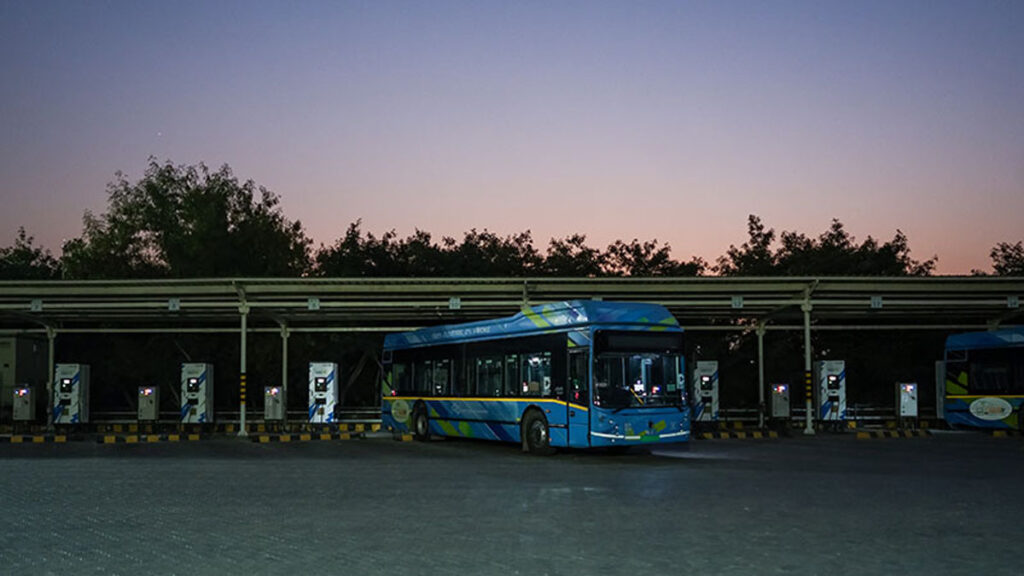
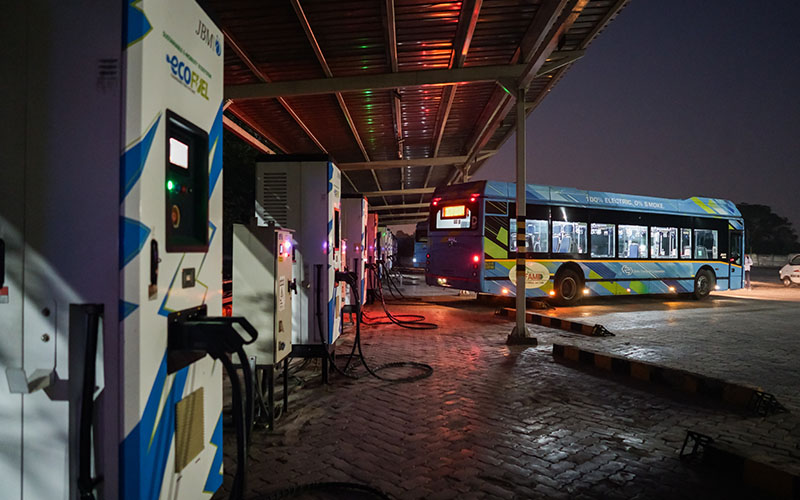
Accelerating e-Bus Deployment
- Developed procurement bid documents/contracts for PM’s eBus Sewa
- Facilitated stakeholder consultations for developing innovative business models for scaling up e-Bus deployment
- Facilitating export of ‘Make in India’ electric buses
- Conducted Impact assessment of e-Bus transition
- US -India Payment Security Mechanism


Deployment of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (EVCI)
- Designing and implementing innovative business models such as ‘EV charging as a service ’
- Implementing the ‘Managed Services Partner’ model Supporting the development of public charging stations at railway stations in India & Bhutan
- Establishing renewable energy-based charging infrastructure in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands
- Developing the Charging Station Assessment Tool (CSAT) to identify priority locations for setting up charging infrastructure


Electrification of Four-Wheeler Fleets
- Developing cost economics, impact assessment and business case for enabling the transition to electric 4 wheelers


Access to Finance
- Supporting capital raise transactions


Capacity Building and Workshops
- Developing a Sustainable Transportation Roadmap for Bhutan
- Organizing study trips on e-Mobility for South Asian countries
- Developing a knowledge series for South Asian utilities on EV integration



